Maths Objects
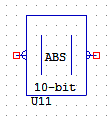
ABSVAL10
The ABSVAL object has a single analogue input and a single analogue output. This object takes the absolute value of the analogue value on its input and outputs it. This object is to be used only in conjunction with certain modules that can return negative analogue values.
Returns a module value that’s 0 at 512 into an always positive value referenced from 512; less than 512 would be negative, greater than 512 is positive.
ABSVAL10 takes the absolute value of a 2’s compliment 10-bit analogue input.
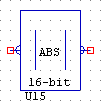
ABSVAL16
ABSVAL16 takes the absolute value of a 2’s compliment 16-bit analogue input. It operates as per ABSVAL10 but zero “0” is now at 32272. Less is negative and greater is positive, with a maximum of 64,544.
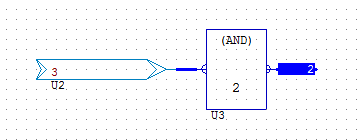
ADD
ADD adds two analogue values together (Output = Top plus bottom). The ADD object has two analogue inputs and a single analogue output. The object adds the analogue values together on pin 1 and pin 2 and outputs the sum.
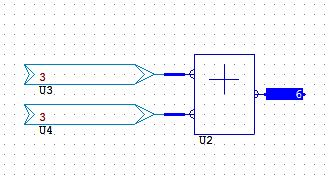
Example: 3+3 equals 6
ADDCONST
ADDCONST adds a constant to an analogue value. The constant is set in object properties.
Add the value 8 to an analogue input:
ANALOG2, ANALOG3, ANALOG4, ANALOG8, ANALOG16
ANALOG converts “X” digital inputs into an analogue value. It performs the opposite task of the BINARY object.
For example an ANALOG2 has possible outputs of 0,1,2,3, whereas the ANALOG16 can output an analogue value up to 255.
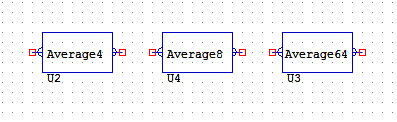
AVERAGE4, 8 & 64
The AVERAGE objects have a single analogue input and a single analogue output. This object does arithmetic of 4, 8 or 64 on the input value and then outputs the new value.
Analogue value average/integrator. (Arithmetic x4)
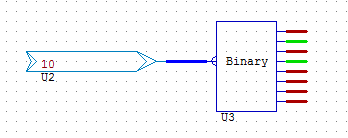
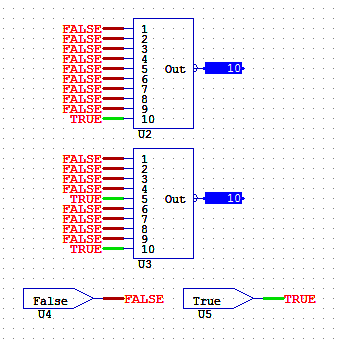
BINARY8 & 16
BINARY decodes up to 8-bit (or 16-bit) value into its corresponding bits. It performs the opposite task of the ANALOG object.
The value 10 is converted to its binary equivalent:
BITANDCONSTANT
Bitwise AND of an analogue value.
Constant is set in Object Properties.
A BITANDCONSTANT takes two binary representations of equal length and performs the logical AND operation on each pair of corresponding bits. In each pair, the result is 1 if the first bit is 1 AND the second bit is 1. Otherwise, the result is 0.
For example:
0101 (Analogue Input binary 5)
AND 0011 (Constant set in properties binary 3)
= 0001 (Result binary 1)
The BITANDCONSTANT may be used to perform a bit mask operation. This operation may be used to isolate part of a string of bits, or to determine whether a particular bit is 1 or 0. For example, given a bit pattern: 0011
To determine whether the third bit is 1, a BITANDCONSTANT is applied to it and another bit pattern containing 1 in the third bit:
0011 (Binary 3)
AND 0010 (Binary 2)
= 0010 (Binary 2)
Since the result is 0010 (non-zero), the third bit in the original pattern was 1.
Using BITANDCONSTANT in this manner is called bit masking, by analogy to the use of masking tape to cover, or mask, portions that should not be altered, or are not of interest. In this case, the 0 values mask the bits that are not of interest.
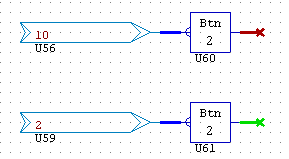
BUTTON
BUTTON decodes an analogue button output to digital based on a constant. The constant is set in the object properties. In the example below 2 is the constant, and the output will go high when 2 is inputted to the device.
In this example the constant is 2. With 10 on the input the output remains low (Brown). When the input is changed to 2 the output goes high (Green).
BYTEBOTH
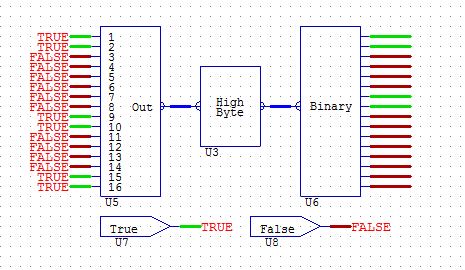
BYTEHIGH
BYTELOW
BYTETOPERCENT
COMBINEBYTES
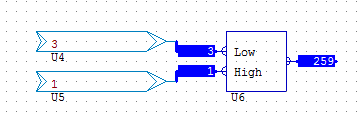
COMBINEBYTES combines two 8-bit bytes into one 16-bit value.
In the example below, the value of the first byte is 3 and the second 1. When these are combined the result is 259, which we can see displayed back as a binary using an analogue to binary conversion.
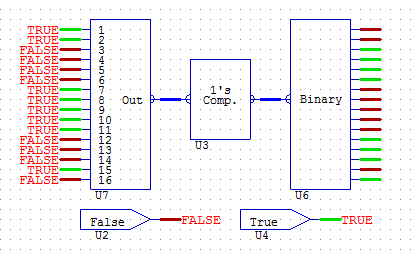
COMPLIMENT
COMPLIMENT takes the compliment of a 16-bit analogue input.
The following illustrates the binary result with the COMPLIMENT function on an analogue input:
CONVERTTIME
DEBOUNCE
DEC
DECODE8, 10, 12, 16, 30, 32, 40
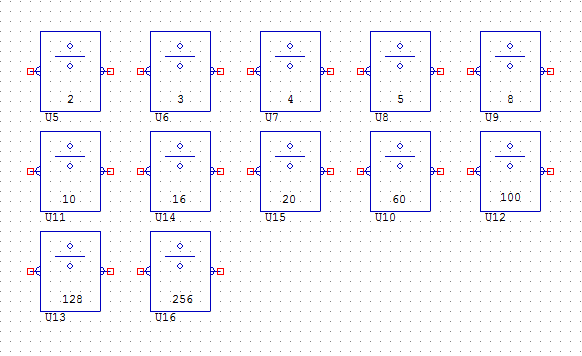
DIVIDE2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 10, 16, 20, 60, 100, 128, 256
The DIVIDE objects have a single analogue input and a single analogue output. The object divides the input value by the amount specified by the object and outputs it.
ENCODE10, 20, 32, 40, 64, 80
ENCODE10 encodes up to ten digital inputs into a normally zero analogue output. Also available in 20, 32, 40, 64 and 80 input versions.
ENCODE outputs a value based on the input selection, where highest selection takes priority.
FAHTOCEL
INC
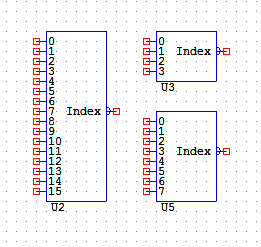
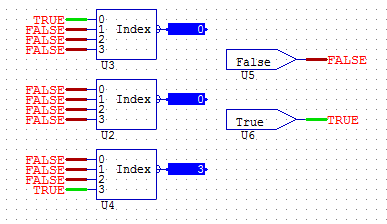
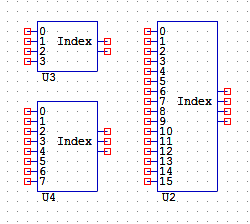
INDEX4, 8, 16
Four Channel Index Selectors:
INDEX will output an analogue between 0 and 3 based on the input selection. If no inputs are selected the device outputs zero, and if input zero is selected the device outputs zero.
INDEX4D, INDEX16D, INDEX8D
INPUTCOUNT8, 16
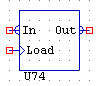
LATCHANALOG
LATCHANALOG is an analogue buffer with load input.
The analogue value on the input is transferred to the output on the transition of a signal on the load input.
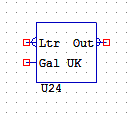
LTRTOGAL
LTRTOGALUK
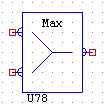
MAX
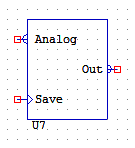
MEMORYANALOG
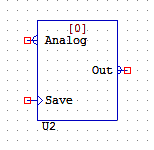
MEMORYANALOGDEF
MEMORYANALOGDEF acts similarly to MEMORYANALOG, in the sense that it will save and output the value on the analogue pin whenever the save pin is high. The difference between the two is with MEMORYANALOGDEF you can start with a predetermined value, rather than zero.
MEMORYDIGITAL
MEMORYTEMPER
MIN
MULTIPLY
The MULTIPLY objects have a single analogue input and a single analogue output. The object multiplies the input value by the amount specified by the object and outputs it. These objects come in five different versions that can multiply by 2, 4, 8 or 16.
The object multiplies two analogue values together (Output= Top x Bottom)
MULTIPLY2, 4, 8, 10, 16
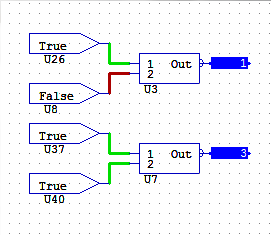
MUX
The MUX objects come in several different varieties that MUX together varying amounts of analogue inputs. The simplest one selects from two analogue values. When the top digital input is false the first value is outputted. When the input is true the second value is outputted. The higher capacity MUX’s use analogue inputs to control which of the inputs is currently being outputted. A value of zero selects the first input; a value of one selects the second input and so on.
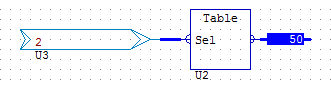
- MUX Analogue Multiplexor
The basic MUX enables selection of two input values via a binary input. With O on the SEL input, the top analogue value appears on the output. With a 1 on the SEL the lower value is now passed to the output.
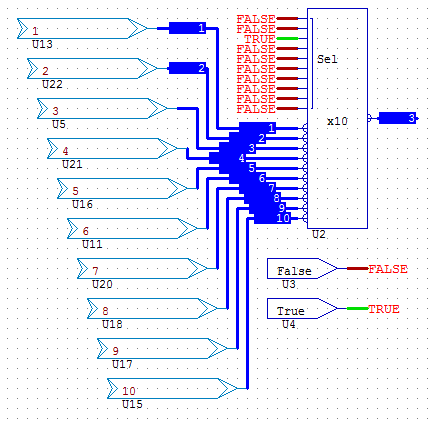
- MUX10 10 Channel Analogue Multiplexor (Available in 4, 8,10,12,32 versions)
In this example changing the value on the analogue SEL input, selects a different input channel, the MUX10 has an input range from 0 to 9. Values greater than the max automatically default to the max channel.
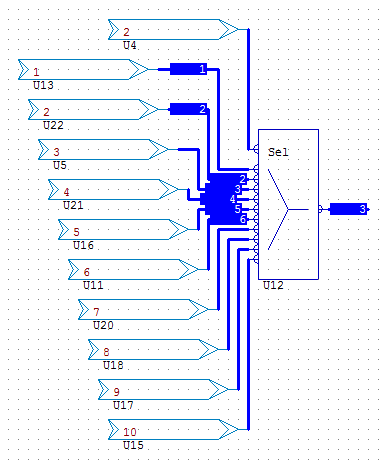
- MUX10S Analogue Selector (Available in,3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 11, 12 Versions)
The MUX10S version has a binary selector, the device will output the highest channel selected in this case the third input is selected. If no input is selected the MUX retains the previous value outputted.
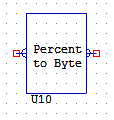
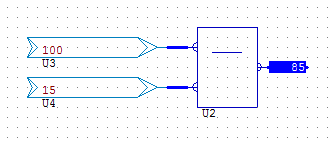
PERCENTTOBYTE
SUBTRACT
The SUBTRACT object has two analogue inputs and a single analogue output. This object subtracts the analogue value on pin 2 from the value on pin 1 and outputs it.
The object subtracts the lower value from the upper value.
In this example we subtract 10 from 255 with the result 245 outputted.
SUBTRACTCONST
SUBTRACTCONST subtracts a constant from an analogue value. The constant is set in object properties.